Unpleasant pain in the lumbar region and spine is in most cases associated with a disease such as osteochondrosis. It affects 40% of men and women aged 30-40 and 90% of the elderly. Therefore, the earlier the disease is diagnosed, the more thoroughly the patient is examined, the more likely they are to stop the progression of osteochondrosis and maintain activity at an older age.
Definition of the disease, the cause of the disease
So what is osteochondrosis, where does it develop, what structures are affected, what is the method of treatment? The disease affects the tissues of the spine and vertebrae and is expressed in violation of their shape, density, elasticity, and sometimes integrity. As a result, the distance between the vertebrae decreases, the spinal column gradually loses its stability, nerve stings, and hernia formation can develop, which is accompanied by back pain and discomfort during movement.
If we briefly describe the essence of osteochondrosis, it is the gradual wear of the tissues of the intervertebral discs (cartilage) that leads to spinal instability. If left untreated, ligaments and joints break down, osteophytes appear, posture is disturbed, and movements are accompanied by pain.
Causes of osteochondrosis of the spine:
- inactive lifestyle with lack of muscle strain;
- spinal cord injury;
- systematic intense stress on the spine;
- heredity;
- overweight;
- hypothermia;
- hormonal and autoimmune diseases;
- toxic poisoning;
- congenital connective tissue failure;
- psychosomatic causes (stress, depression, etc. ).
Symptoms of osteochondrosis
The disease is characterized by periods of remission and exacerbation, with varying degrees of severity of symptoms. The main symptoms of osteochondrosis of the spine, which are characteristic of the main types of disease, are the lumbar, cervical and thoracic:
- pain localized in a specific area of the spine;
- reflected-type pain syndrome with damage to nearby locomotor tissues;
- myelopathy and radiculopathy resulting from compression of the nerve endings in the spinal cord and blood vessels.
Depending on which part of the spine is affected by the disease, the list of symptoms of osteochondrosis may vary. Namely: patients notice muscle tingling, limb numbness, other sensory disorders, decreased arm and leg strength, head and heart pain, sore back pain.
Pathogenesis of osteochondrosis
Before the elastic fibrous core of the intervertebral disc loses its elasticity and deforms, osteochondrosis performs several processes in the human body:
- convulsions, dystonia, inflammation;
- decreased blood circulation;
- damage to neuronal processes.
Furthermore, cracks appear on the deformed ring, the discs protrude, and a hernia is formed. Typically, these indicators of spinal disease develop in childhood or adolescence and are often the result of poor posture, scoliosis, sports injuries, infectious diseases, or congenital vascular disease.

Stages of osteochondrosis
There are three stages in the development of spinal osteochondrosis:
- the first, in which the height of the intervertebral disc begins to decrease, acquiring a flattened shape, loses moisture, elasticity, can protrude;
- the second develops in the absence of treatment and manifests itself in violation of the structure of the fibrous ring of the vertebral disc, the appearance of cracks, and the development of instability in certain areas of the spine;
- it is characterized by rupture of the intervertebral cartilage, the formation of a hernia, and the formation of bone processes in osteophytes.
Symptoms of osteochondrosis of the spine become more intense from the first to the third stage.
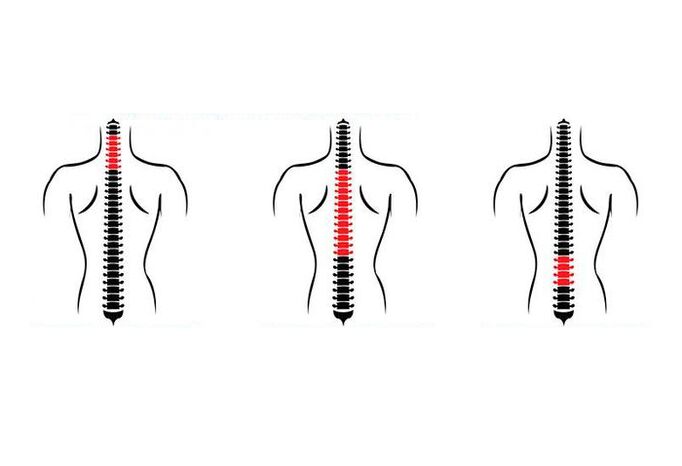
Classification of osteochondrosis
Osteopondrosis is classified on the basis of several signals, the main one being the localization zone. Distinguish:
- lumbar osteochondrosis;
- osteochondrosis of the cervical spine;
- osteochondrosis of the thoracic spine.
In osteochondrosis of the lumbar spine, there is pain in the lumbar region, which increases with the rotation of the body and weight lifting. The pain can be given to the foot or to both feet, characterized as painful. In case of acute syndrome, hernia is suspected. In lumbar osteochondrosis, cramps in the muscles of the legs, peeling of the skin, often occur.
With the development of osteochondrosis of the spine, vertebrae 1 to 7 are involved in the cervical spine. The disease is accompanied by headache in the back of the head, pain in the neck, collarbone, shoulders. Bruising is possible during head rotation, numbness of the upper limbs, a lot of sensation in the throat.
In osteochondrosis of the spine in the chest region, the patient is concerned about chest, shoulder, armpit, heart pain. Perhaps a feeling of shortness of breath, the onset of an attack of intercostal neuralgia.
Lumbar spine osteochondrosis is the most common, the chest the least common.
Complications of osteochondrosis
If the patient was thinking too late to treat osteochondrosis when the symptoms of the disease were manifested, the following complications may develop:
- intervertebral hernia;
- spinal cord stroke;
- sphincter of the spine;
- protrusion;
- radiculitis;
- paralysis of the lower extremities.
In the absence of treatment, the patient is regularly aggravated by a condition characterized by increased pain, restraint of movement, and a sharp deterioration in general well-being. The most horrible complication of spinal osteochondrosis is disability. Therefore, high quality and timely treatment of osteochondrosis is needed to prevent such severe changes in musculoskeletal function.
Diagnosis of osteochondrosis
Diseases such as osteochondrosis are primarily pain in the spine. But it is important to distinguish it from pain caused by problems other than degeneration of the intervertebral discs. To do this, doctors make a step-by-step diagnosis that includes:
- Recording of medical history, which includes a conversation between the practitioner and the patient to identify the exact area of localization of pain, factors that provoke deterioration of the condition. It is important to know the patient’s occupation, the period when spinal problems began, when there was an exacerbation, what pain occurs in the lumbar and other regions, what treatment methods the patient used.
- Physiological examinationallows you to determine the proportions of the body, the quality of movements and operations performed, the condition of the skin, the degree of sensitivity to pain. The doctor palpates the condition of the muscle tissue, the presence of seals, edema, and so on.
- X-ray of the spine in two planesfor visual assessment of the condition. It makes it possible to determine the displacement of the vertebrae, the presence of osteophytes, the deposition of salt.
If the data collected to prescribe treatment is insufficient or if there is a suspicion of severe spinal pathology, the patient will be imaged with CT and magnetic resonance imaging, which will allow detailed examination of vertebrae, blood vessels, soft tissues, nerve processes, and complete imaging of osteochondrosis. on the condition of the affected spine to determine tactical treatment.
Treatment of osteochondrosis
Like all diseases, osteochondrosis requires identification of the cause that triggered its development. Reducing the severity of symptoms is not the main but an important stage of treatment, the outcome of which depends on a number of factors. In some cases it is a complete cure, in other cases it is the prevention of complications and disability.
A group of measures is used to treat osteochondrosis of the spine:
- changing the patient's daily routine;
- prescribing medications to reduce symptoms;
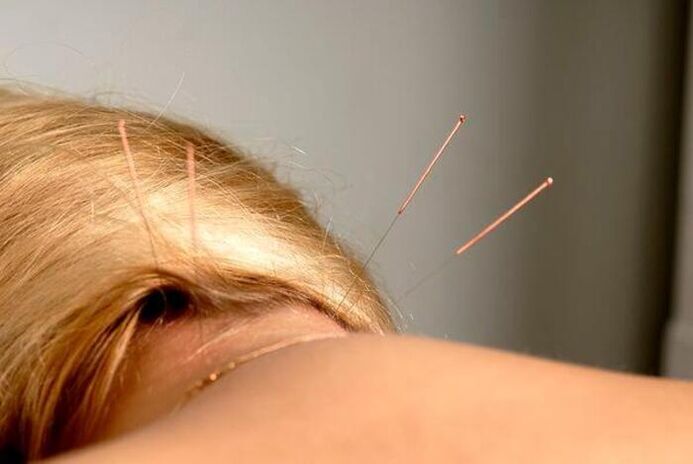
- physiotherapy procedures (massage, acupuncture, electrophoresis, training therapy, etc. ).
Changing the daily routine in the treatment of spinal osteochondrosis includes a decrease in the intensity of physical activity, bed rest with severe pain, and the exclusion of sharp turns and bends.
Medications for the treatment of osteochondrosis of the spine
They can be divided into several groups:
- muscle relaxants to relieve pain, including tablets, injectable anesthetics, and anti-inflammatory injections to treat osteochondrosis. The homeopathic preparation normalizes thyroid function, improves lymphatic drainage, has anti-inflammatory, detoxifying and immunomodulatory effects.
- non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. When used in patients with osteoarthritis, it reduces the progression of inflammatory and destructive changes in the joints, improves cartilage integrity, thickness and other characteristics, and stimulates bone tissue repair.
- anti-inflammatory topical ointments and alternative transdermal patches. Such drugs have analgesic, antirheumatic, antipyretic and anti-inflammatory effects. The mechanism of work is to reduce the production of inflammatory mediators, to reduce body temperature and pain.
- chondroprotectors;
- curative analgesic blockades;
- Vitamins B.
Additional treatments
Among the additional resources that can be used to treat, alleviate, and improve the function of the spinal and intervertebral discs, the following are the most effective:
- acupuncture;
- magnetotherapy;
- professional massage and self-massage;
- physical education courses;
- manual therapy.
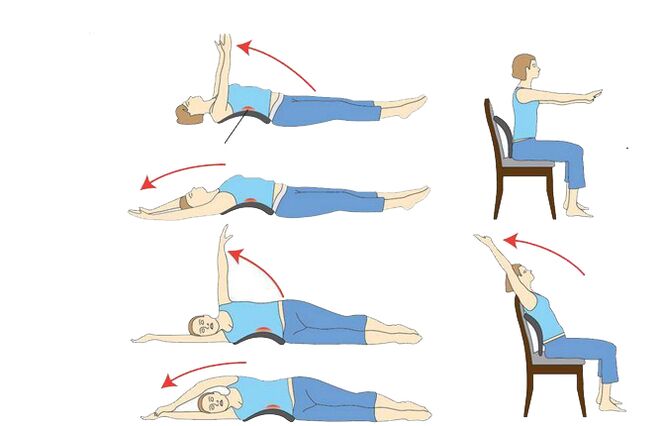
Forecasting, prevention
If spinal disease is not neglected, it continues without serious complications, during 1, 5-2 months of competent treatment the condition can be significantly improved and the transition of the disease to chronic form can be prevented. In severe cases, doctors recommend surgical treatment.
Prevention of spinal osteochondrosis includes:
- maintaining a proper daily routine by changing posture and moderate physical activity;
- regular visits to the pool;
- weight control;
- wearing comfortable shoes;
- balanced diet;
- sleeps on an orthopedic pillow and mattress;
- taking missing nutrients or preventative homeopathic medicines to increase immunity, improve overall health, and eliminate dystonia.
It is necessary to have medical examinations every year and see a doctor immediately for treatment as soon as any pain in the spine appears.
No matter what osteochondrosis we are talking about - lumbar, cervical or chest - paying attention to one’s own health should become a good habit, especially when it comes to the basics of the entire musculoskeletal system - the spine.





































